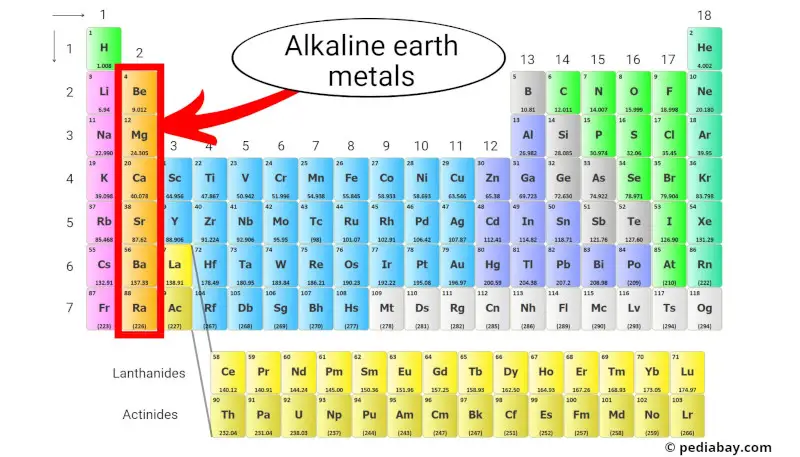
Alkaline earth metals are a group of elements located in the second column of the periodic table. They include beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
These metals have two electrons in their outermost shell, [1] making them chemically reactive but not as reactive as alkali metals, which are in the first column.
Let’s explore more about the alkaline earth metals of the periodic table.
Table of contents:
- What are alkaline earth metals?
- What is common between all the alkaline earth metals?
- List of alkali metals and their electron configurations
- Periodic trends of alkaline earth metals
- Summary
What are alkaline earth metals?

Alkaline earth metals are a group 2 elements of the periodic table and they have two special characteristics.
- When they react with water, they produce hydroxides that are alkaline or basic in nature.
- Their oxide minerals (BeO, magnesite, MgO, beryl, etc) are mostly found from the earth crust and are stable to heat.
Explanation
When the alkaline earth metals (Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba and Ra) react with water, they form hydroxides which are alkaline (or basic) in nature. [2]
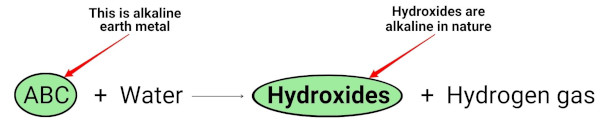
You can see in the above chemical equation that the alkali metals give hydroxides which are basic (having pH > 7) in nature and liberate the hydrogen gas.
For example:
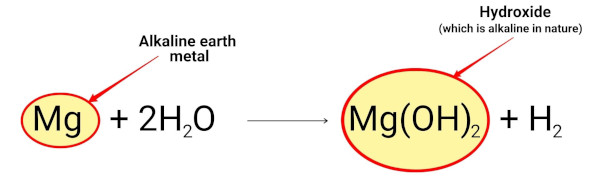
Magnesium reacts with water and forms magnesium hydroxide which is alkaline in nature.
Also, these metals are mostly found from the earth crust (in their oxides form) and these oxide minerals are stable to heat. [2]
These two criteria give these metals their name “alkaline earth metals”.
(Note: It’s important to note that beryllium, which is also a group 2 element, does not form an alkaline solution when reacting with water. Instead, its hydroxides show amphoteric behavior, which means they can behave as either an acid or a base. Therefore, beryllium is not considered an alkaline earth metal even though it’s in the same group.)
What is common between all the alkaline earth metals?
Alkaline earth metals share several common traits.
For instance, they all have two valence electrons in their outermost energy level, which makes them quite reactive.
This reactivity is because of the tendency to lose these electrons in chemical reactions, resulting in the formation of cations with a +2 charge.
Additionally, all the alkaline earth metals have a silvery-white and shiny appearance.

So these are the two main things that the alkaline earth metals have in common.
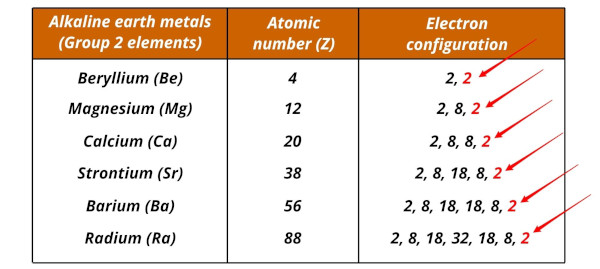
List of alkali metals and their electron configurations
The alkaline earth metals and their electron configurations are given below.
| Element | Electron configuration |
| Beryllium (Be) | [He] 2s2 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | [Ne] 3s2 |
| Calcium (Ca) | [Ar] 4s2 |
| Strontium (Sr) | [Kr] 5s2 |
| Barium (Ba) | [Xe] 6s2 |
| Radium (Ra) | [Rn] 7s2 |
Periodic trends of alkaline earth metals
As we move down the group of alkaline earth metals on the periodic table, the following trends can be observed:
- Valency: All alkaline earth metals have the same valency of +2. So there is no change in valency as we move down the group.
- Atomic size: The atomic size of alkaline earth metals increases as we move down the group. This is because there is an increase in the number of electron shells (or orbits), and the shielding effect of inner electrons reduces the attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
- Metallic character: The metallic character of alkaline earth metals increases as we move down the group. This is because the atoms become larger and have more electrons, making them more easily able to lose electrons and form positive ions.
- Electronegativity: The electronegativity of alkaline earth metals decreases as we move down the group. This is because the atoms become larger and have more electron shells, making it harder for them to attract electrons towards themselves.
- Electron affinity: The electron affinity of alkaline earth metals is generally low, and it decreases as we move down the group.
- Ionization energy: The ionization energy of alkaline earth metals decreases as we move down the group. This is because the larger atoms have more electron shells, and the outermost electrons are farther away from the nucleus, making them easier to remove.
Summary
Alkaline earth metals include beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. They have two electrons in their outermost shell, making them reactive but less so than alkali metals.
These metals produce alkaline hydroxides when reacting with water and have oxide minerals that are stable to heat. The main characteristics shared by all alkaline earth metals include having two valence electrons, being silvery-white and shiny, and forming cations with a +2 charge.
The valency remains the same as we move down the group, but the atomic size and metallic character increase, while the electronegativity, electron affinity, and ionization energy decrease.
External resources:
- Alkaline-earth metal | Properties, List, & Reactivity. (n.d.). Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/alkaline-earth-metal
- Alkaline earth metal – Wikipedia. (2012, November 1). Alkaline Earth Metal – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alkaline_earth_metal
- Boudreaux, K. A. (n.d.). The Parts of the Periodic Table. The Parts of the Periodic Table. http://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/periodic/periodic_main2.htm
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. He is a founder of Pediabay and is passionate about helping students through his easily digestible explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.