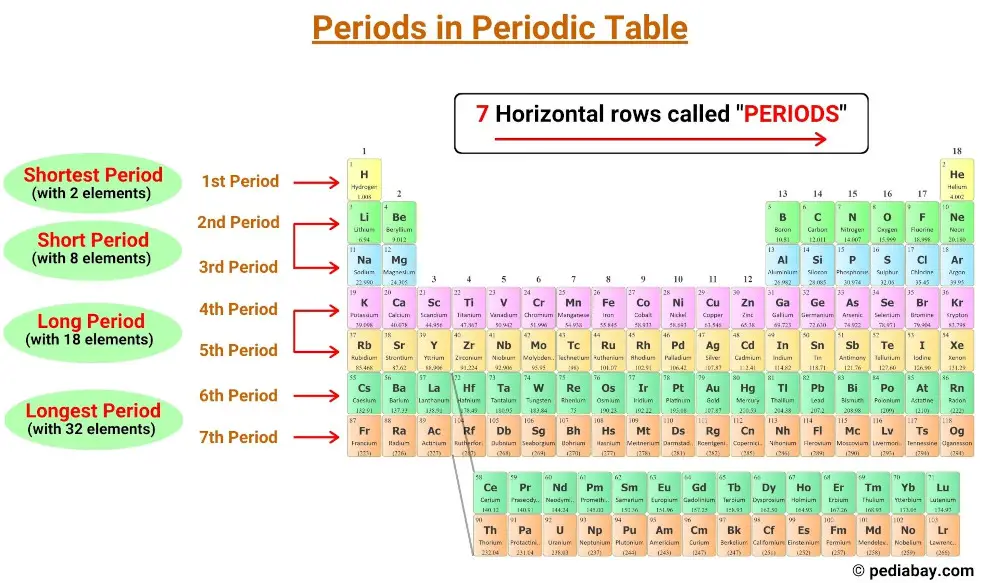
The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called periods and there are 7 periods in the periodic table.
The elements lying in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Let’s explore more about the periods of the periodic table.
Table of contents:
- What are periods in the periodic table?
- Characteristics of elements in periods
- Importance of periods in chemistry
- Summary
What are periods in the periodic table?
In the periodic table, periods are the rows that run horizontally from left to right.
The periodic table is organized so that elements with similar properties are grouped together in columns called groups or families, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
There are seven periods in the periodic table, numbered 1 through 7. [1]
Number of shells of an element and its period number
The number of shells of an element determines its period in the periodic table.
For example, elements in period 1 have only one electron shell, while elements in period 2 have two electron shells, and so on.
This organization helps chemists predict the properties of an element based on its location in the periodic table.
Characteristics of elements in periods
As you move across a period in the periodic table, there are several characteristics of elements that change in predictable ways. This is due to the periodic trends that are observed in the properties of elements.
Atomic radius:
As you move from left to right across a period, the atomic radius generally decreases. [2]
This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, causing a greater attraction between the nucleus and the electrons in the outermost energy level. This results in a smaller atomic radius.
Electronegativity:
Electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
As you move from left to right across a period, electronegativity generally increases. [3]
This is because the atomic radius is smaller and the positive charge of the nucleus is stronger, making it more attractive to negatively charged electrons.
Ionization energy:
Ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
As you move from left to right across a period, ionization energy generally increases. [4]
This is because the atomic radius is smaller and the electrons are held more tightly by the nucleus, making it more difficult to remove an electron.
Other characteristics:
Melting and boiling points: Generally increase from left to right across a period, but with some exceptions.
Metallic character: Decreases from left to right across a period, as nonmetals become more prevalent.
Reactivity: Elements become less reactive as you move from left to right across a period, as the electrons are held more tightly and are less likely to participate in chemical reactions.
Importance of periods in chemistry
Periods in the periodic table are essential in understanding the behavior of elements, as they provide information about the electron configuration of elements and how they interact with other elements. Here are some ways in which periods are important in chemistry:
- Predicting properties: The periodic table allows scientists to predict the properties of elements based on their position in the table. For example, elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells, which can help predict their atomic size, reactivity, and other properties.
- Identifying trends: The arrangement of elements in the periodic table allows scientists to identify trends in their properties. For example, electronegativity and ionization energy tend to increase from left to right across a period, while atomic size tends to decrease. This information can be used to make predictions about the behavior of elements in chemical reactions.
- Grouping elements: The periodic table groups elements into categories based on their properties, such as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. This helps scientists understand the similarities and differences between elements and how they interact with each other.
- Discovering new elements: The periodic table also helps scientists predict the existence and properties of new elements. By looking at gaps in the table, scientists can predict the properties of undiscovered elements and search for them in the laboratory.
Summary
The periodic table has seven horizontal rows called periods. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. There are seven periods in the periodic table, numbered 1 through 7, and the number of shells of an element determines its period.
As you move across a period in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally decreases, while electronegativity and ionization energy generally increase. Other characteristics such as melting and boiling points, metallic character, and reactivity also change predictably across a period.
Periods in the periodic table are important in predicting the properties of elements, identifying trends, grouping elements, and discovering new elements. By looking at gaps in the table, scientists can predict the properties of undiscovered elements and search for them in the laboratory.
External resources:
- Period | chemistry. (n.d.). Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/period-chemistry
- Period (periodic table) – Wikipedia. (2008, February 5). Period (Periodic Table) – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Period_(periodic_table)
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. He is a founder of Pediabay and is passionate about helping students through his easily digestible explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.