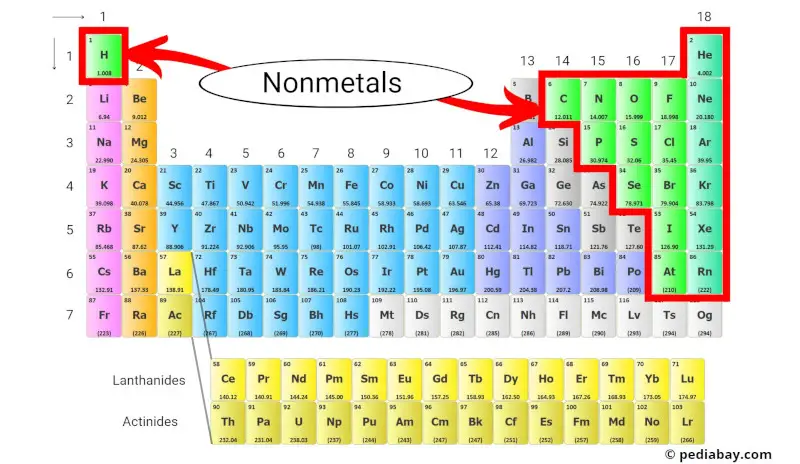
Nonmetals are a group of elements that lack the properties of metals, such as high electrical conductivity and luster. These nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table, with the exception of hydrogen.
Nonmetals can be found in various forms, including gases like oxygen and chlorine, liquids like bromine, and solids like sulfur and carbon. [1]
Let’s see more important things about nonmetals.
Table of contents:
- What exactly are the nonmetals?
- List of nonmetals present on the periodic table
- State of non metals (solid, liquid or gas?)
- Most reactive nonmetal
- Role of nonmetals in environmental and industrial applications
What exactly are the nonmetals?
Nonmetals are elements that have a tendency to gain electrons in chemical reactions, forming negatively charged ions or anions.
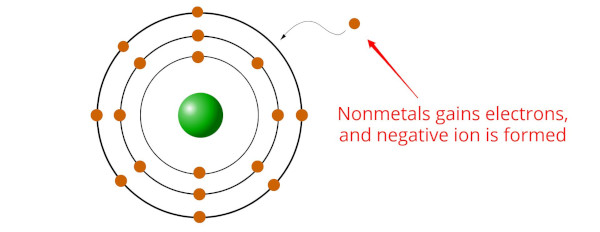
This is because nonmetals typically have a higher electronegativity than metals, [2] meaning they have a greater attraction for electrons.
When nonmetals bond with metals, the nonmetallic element gains one or more electrons from the metal to form a stable compound.
For example, chlorine gains one electron from sodium to form the ionic compound sodium chloride (NaCl).
We can also say that – Nonmetals are a group of chemical elements that lack the physical and chemical properties of metals.
Well, let’s see the list of nonmetals present on the periodic table.
List of nonmetals present on the periodic table
Here is a list of nonmetals present on the periodic table:
- Hydrogen (H)
- Helium (He)
- Carbon (C)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
- Neon (Ne)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Sulfur (S)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Argon (Ar)
- Selenium (Se)
- Bromine (Br)
- Krypton (Kr)
- Iodine (I)
- Xenon (Xe)
- Astatine (At)
- Radon (Rn)
These nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table, except for hydrogen, which is located at the top of the periodic table above the alkali metals.
State of non metals (solid, liquid or gas?)
Nonmetals can exist in all three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
The state of a nonmetal depends on the temperature and pressure conditions it is exposed to.
Out of all the nonmetals of the periodic table;
- 11 non metals are in gaseous state at room temperature. [3]
- Bromine (Br) is a nonmetal which is in liquid state at room temperature.
- Rest of the nonmetals are solids at room temperature.
Most reactive nonmetal
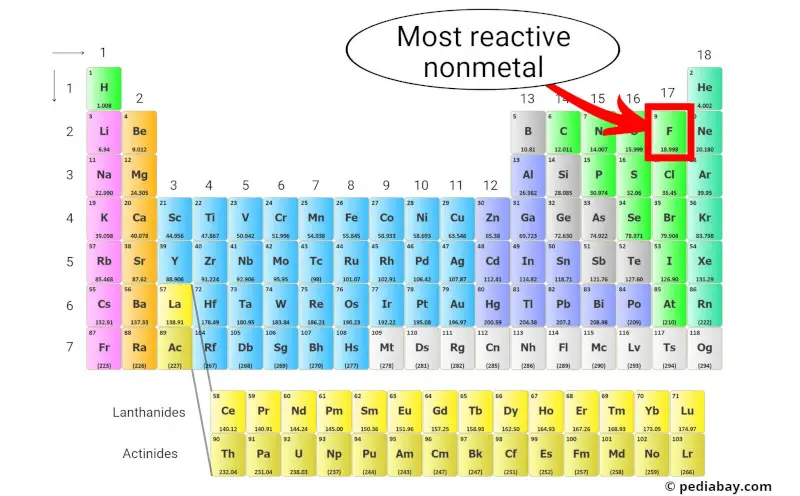
Fluorine (F) is the most reactive nonmetal present on the periodic table.
But why? What is the reason for fluorine being the most reactive?
This is because it has the highest electronegativity of any element, meaning it has a strong attraction for electrons.
Fluorine has seven electrons in its outermost energy level and requires one more electron to fill its valence shell and achieve a stable configuration.
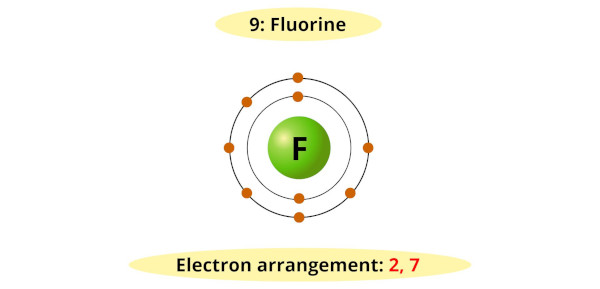
Therefore, it readily accepts an electron from other elements to form a fluoride ion (F-).
Due to its high reactivity, fluorine can react explosively with many other elements and compounds, including water, metals, and even glass. [4]
Fluorine is so reactive that it is typically stored and transported in specialized containers made of materials that are resistant to its corrosive properties.
Role of nonmetals in environmental and industrial applications
Nonmetals are used in various industrial processes and environmental applications due to their unique properties. Here are some examples:
- Air pollution control: Nonmetals such as nitrogen and oxygen play a vital role in air pollution control. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are harmful pollutants released from vehicles and industrial processes. Nonmetal-based catalysts are used to convert NOx into harmless gases like nitrogen and water. Similarly, oxygen is used in combustion processes to reduce harmful emissions.
- Fertilizers: Nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur are essential nutrients for plant growth. Nonmetal-based fertilizers like ammonium nitrate and superphosphate are widely used in agriculture to increase crop yields.
- Batteries: Nonmetallic elements such as sulfur, carbon, and lithium are used in batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in electronic devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems.
- Water purification: Nonmetals like chlorine and iodine are commonly used as disinfectants in water purification systems. They kill harmful bacteria and viruses and make water safe for consumption. [5]
- Chemical manufacturing: Nonmetals such as sulfur and chlorine are widely used in the production of chemicals like sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and chlorine-based solvents.
Summary
Nonmetals lack the properties of metals such as high electrical conductivity and luster and are located on the right side of the periodic table except for hydrogen. They exist in all three states of matter depending on temperature and pressure conditions.
Fluorine is the most reactive nonmetal due to its high electronegativity and readily accepts an electron from other elements to form a fluoride ion (F-).
Nonmetals have several uses in environmental and industrial applications, including air pollution control, fertilizers, batteries, water purification, and chemical manufacturing.
External resources:
- Foundation, C. (n.d.). CK12-Foundation. CK12-Foundation. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-middle-school-physical-science-flexbook-2.0/section/4.4/primary/lesson/nonmetals-ms-ps
- Yao, B., Kuznetsov, V. L., Xiao, T., Slocombe, D. R., Rao, C. N. R., Hensel, F., & Edwards, P. P. (2020, August 17). Metals and non-metals in the periodic table. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 378(2180), 20200213. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2020.0213
- Boudreaux, K. A. (n.d.). The Parts of the Periodic Table. The Parts of the Periodic Table. https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/periodic/physical_metals.htm
- Nonmetal – Wikipedia. (2022, August 27). Nonmetal – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nonmetal
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. He is a founder of Pediabay and is passionate about helping students through his easily digestible explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.

