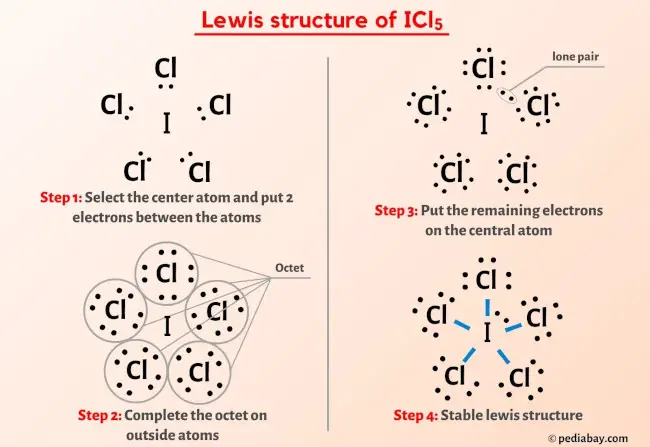
So you have seen the above image by now, right?
Let me explain the above image in short.
ICl5 lewis structure has an Iodine atom (I) at the center which is surrounded by five Chlorine atoms (Cl). There are 5 single bonds between the Iodine atom (I) and each Chlorine atom (Cl). There are 3 lone pairs on all the Chlorine atoms (Cl) and 1 lone pair on the Iodine atom (I).
If you haven’t understood anything from the above image of ICl5 (iodine pentachloride) lewis structure, then just stick with me and you will get the detailed step by step explanation on drawing a lewis structure of ICl5.
So let’s move to the steps of drawing the lewis structure of ICl5.
Steps of drawing ICl5 lewis structure
Step 1: Find the total valence electrons in ICl5 molecule
In order to find the total valence electrons in a ICl5 (iodine pentachloride) molecule, first of all you should know the valence electrons present in iodine atom as well as chlorine atom.
(Valence electrons are the electrons that are present in the outermost orbit of any atom.)
Here, I’ll tell you how you can easily find the valence electrons of iodine as well as chlorine using a periodic table.
Total valence electrons in ICl5 molecule
→ Valence electrons given by iodine atom:
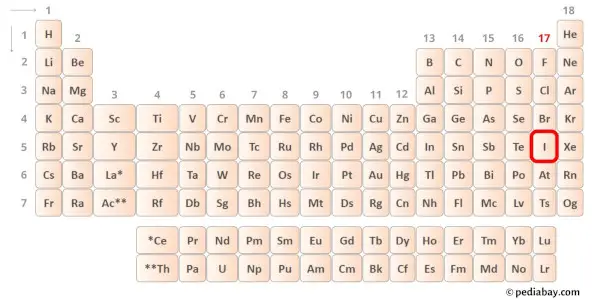
Iodine is a group 17 element on the periodic table. [1] Hence the valence electrons present in iodine is 7.
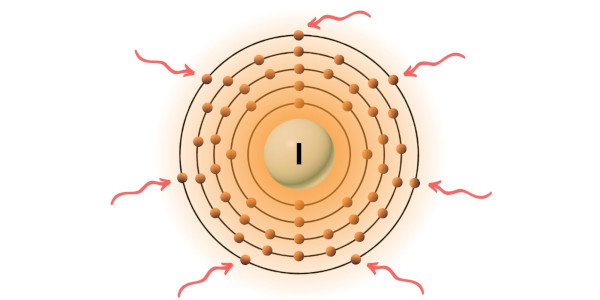
You can see the 7 valence electrons present in the iodine atom as shown in the above image.
→ Valence electrons given by chlorine atom:
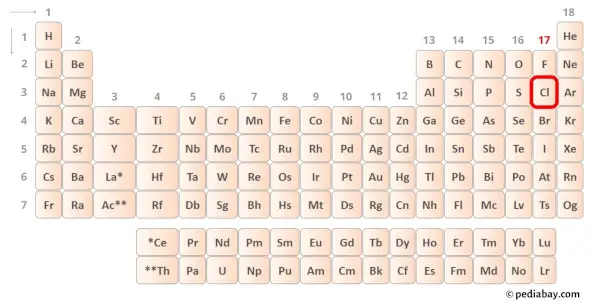
Chlorine is group 17 element on the periodic table. [2] Hence the valence electrons present in chlorine is 7.
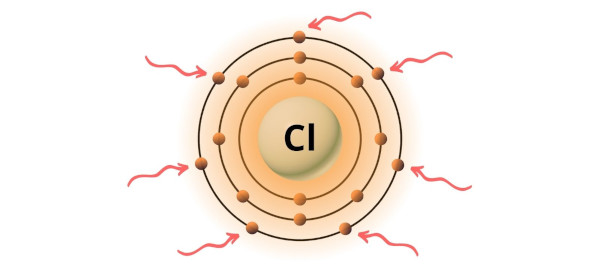
You can see the 7 valence electrons present in the chlorine atom as shown in the above image.
Hence,
Total valence electrons in ICl5 molecule = valence electrons given by 1 iodine atom + valence electrons given by 5 chlorine atoms = 7 + 7(5) = 42.
Step 2: Select the central atom
For selecting the center atom, you have to remember that the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center.
Now here the given molecule is ICl5 (iodine pentachloride) and it contains iodine atom (I) and chlorine atoms (Cl).
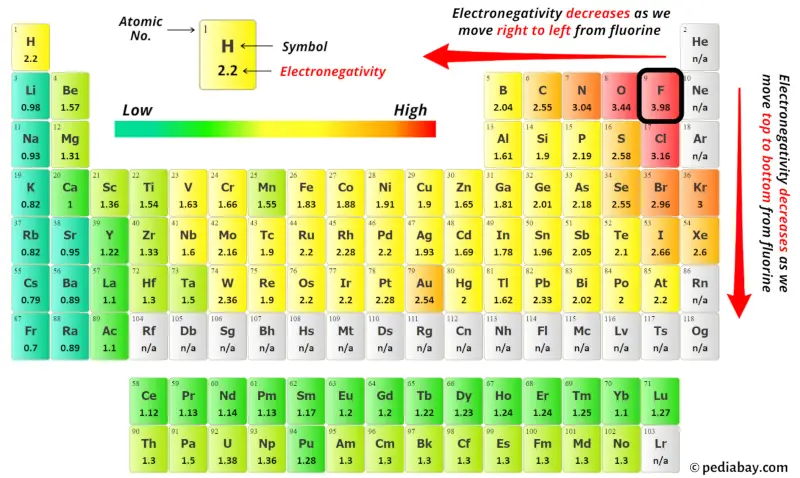
You can see the electronegativity values of iodine atom (I) and chlorine atom (Cl) in the above periodic table.
If we compare the electronegativity values of iodine (I) and chlorine (Cl) then the iodine atom is less electronegative.
So here the iodine atom (I) is the center atom and the chlorine atoms (Cl) are the outside atoms.
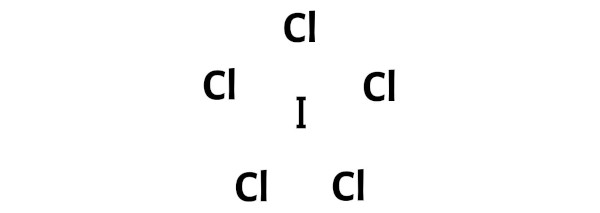
Step 3: Connect each atoms by putting an electron pair between them
Now in the ICl5 molecule, you have to put the electron pairs between the iodine atom (I) and chlorine atoms (Cl).
This indicates that the iodine (I) and chlorine (Cl) are chemically bonded with each other in a ICl5 molecule.
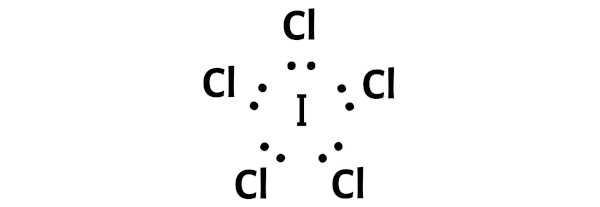
Step 4: Make the outer atoms stable. Place the remaining valence electrons pair on the central atom.
Now in this step, you have to check the stability of the outer atoms.
Here in the sketch of ICl5 molecule, you can see that the outer atoms are chlorine atoms.
These outer chlorine atoms are forming an octet and hence they are stable.
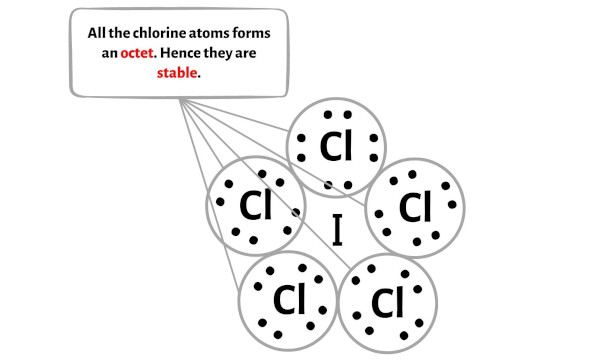
Also, in step 1 we have calculated the total number of valence electrons present in the ICl5 molecule.
The ICl5 molecule has a total 42 valence electrons and out of these, only 40 valence electrons are used in the above sketch.
So the number of electrons which are left = 42 – 40 = 2.
You have to put these 2 electrons on the central iodine atom in the above sketch of ICl5 molecule.
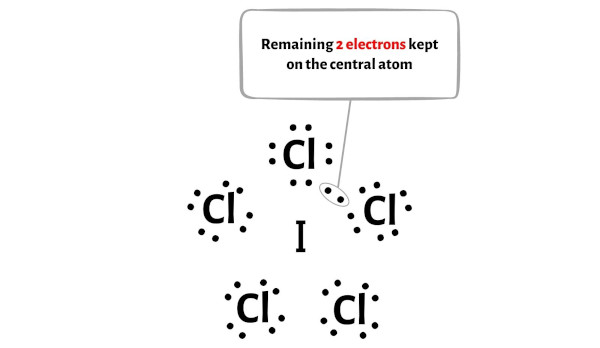
Now let’s proceed to the next step.
Step 5: Check the stability of lewis structure
Now you have come to the final step in which you have to check the stability of lewis structure of ICl5.
The stability of lewis structure can be checked by using a concept of formal charge.
In short, now you have to find the formal charge on iodine (I) atom as well as chlorine (Cl) atoms present in the ICl5 molecule.
For calculating the formal charge, you have to use the following formula;
Formal charge = Valence electrons – (Bonding electrons)/2 – Nonbonding electrons
You can see the number of bonding electrons and nonbonding electrons for each atom of ICl5 molecule in the image given below.
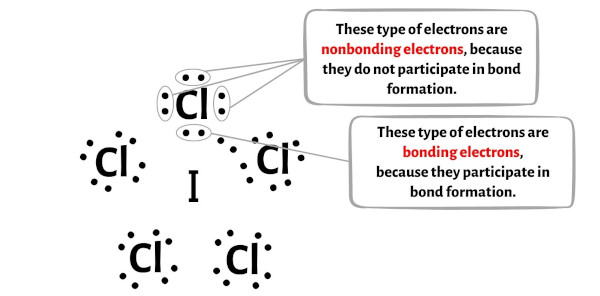
For Iodine (I) atom:
Valence electrons = 7 (because iodine is in group 17)
Bonding electrons = 10
Nonbonding electrons = 2
For Chlorine (Cl) atom:
Valence electrons = 7 (because chlorine is in group 17)
Bonding electrons = 2
Nonbonding electrons = 6
| Formal charge | = | Valence electrons | – | (Bonding electrons)/2 | – | Nonbonding electrons | ||
| I | = | 7 | – | 10/2 | – | 2 | = | 0 |
| Cl | = | 7 | – | 2/2 | – | 6 | = | 0 |
From the above calculations of formal charge, you can see that the iodine (I) atom as well as chlorine (Cl) atoms have a “zero” formal charge.
This indicates that the above lewis structure of ICl5 is stable and there is no further change in the above structure of ICl5.
In the above lewis dot structure of ICl5, you can also represent each bonding electron pair (:) as a single bond (|). By doing so, you will get the following lewis structure of ICl5.
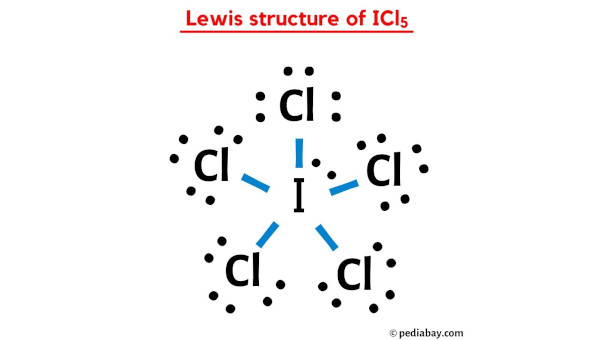
I hope you have completely understood all the above steps.
For more practice and better understanding, you can try other lewis structures listed below.
Try (or at least See) these lewis structures for better understanding:
| NH2Cl Lewis Structure | CHO2- Lewis Structure |
| PF6- Lewis Structure | CNO- Lewis Structure |
| BrO2- Lewis Structure | N2O4 Lewis Structure |
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. He is a founder of Pediabay and is passionate about helping students through his easily digestible explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.