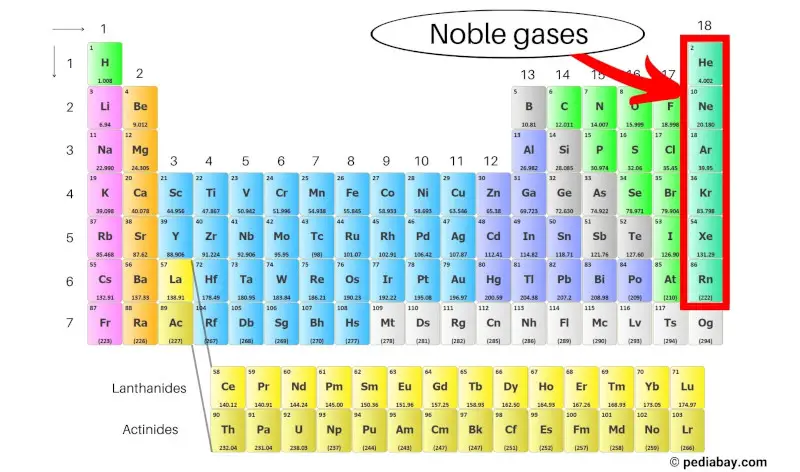
The noble gases, also known as the inert gases, are a group of elements located in the far right column of the periodic table. They include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn).
These elements are known for their low reactivity due to their full outermost electron shells, making them stable and nonreactive with other elements. [1]
Let’s explore more about the noble gases of the periodic table.
Table of contents:
- What are noble gases?
- Why are noble gases inert?
- List of noble gases and their electron configurations
- What is common between all the noble gases?
- Summary
What are noble gases?
Noble gases are group 18 elements that are characterized by their very low reactivity with other substances, meaning that they typically do not form compounds with other elements.
They are also known as inert gases because they are very stable and don’t easily react with other substances. The noble gases include helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
Noble gases are found in small amounts in the Earth’s atmosphere, and are used in various applications, such as in lighting, welding, and cryogenics. [2]
Why are noble gases inert?
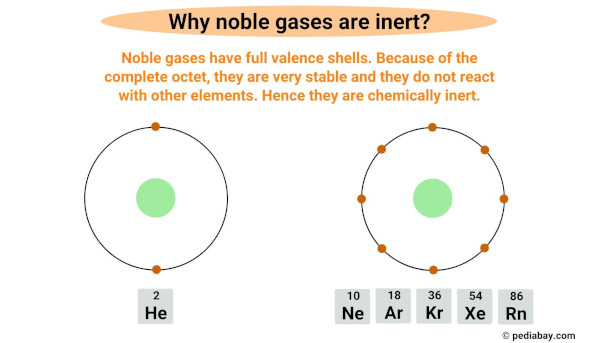
Noble gases are inert or unreactive because they have a full outermost electron shell, also known as valence shell.
The valence shell is the outermost shell of electrons that surrounds an atom and contains its valence electrons, which are the electrons involved in chemical reactions.
Noble gases have a complete octet, meaning they have a full valence shell with eight electrons, except for helium which has only two electrons in its outermost shell.
Having a complete octet makes them very stable and unlikely to react with other elements.
In chemical reactions, elements tend to gain or lose electrons in order to obtain a complete octet in their valence shell, but since noble gases already have a full valence shell, they do not need to gain or lose electrons.
This stable configuration of noble gases is due to their electronic configuration.
The outermost shell of electrons in these elements is full, and so they have no need to gain or lose any electrons.
This means they are very unreactive, and do not tend to form chemical bonds with other elements.
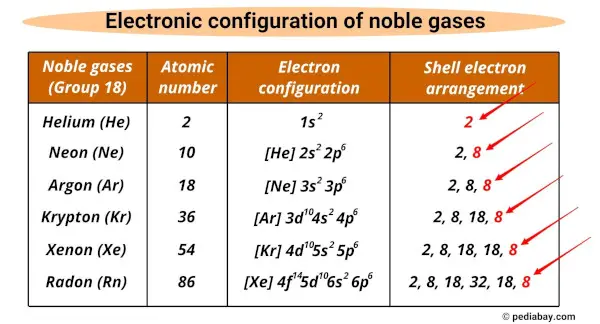
List of noble gases and their electron configurations
The noble gases and their electron configurations are given below.
What is common between all the noble gases?
Noble gases share some common properties.
They all have the same number of valence electrons (i.e 8), except for helium which has 2.
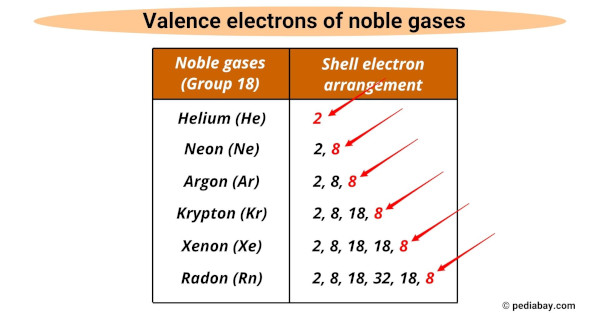
The valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate in chemical reactions, and noble gases have a full valence shell which makes them unreactive.
Additionally, noble gases are colorless gases that we cannot see, and they are also odorless, which means they do not have a smell. [3]
Finally, they exist naturally as monoatomic gases, which means they have only one atom in their elemental form.
Unlike most other elements that tend to form molecules by bonding with other atoms, noble gases have no need to bond with other atoms because they have a full valence shell, which makes them very stable and unreactive.
Summary
Noble gases are a group of elements that are found in the far right column of the periodic table, including helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
They are characterized by their low reactivity due to their full outermost electron shells. Noble gases are inert or unreactive because they have a full valence shell, which makes them very stable and unlikely to react with other elements.
Noble gases share common properties, including the same number of valence electrons (8 except for helium which has 2), colorless and odorless gas, and exist naturally as monoatomic gases.
They are used in various applications such as lighting, welding, and cryogenics, and as coolants in nuclear reactors and fillers for incandescent bulbs.
External resources:
- Noble gas – Wikipedia. (2014, May 30). Noble Gas – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noble_gas
- C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – THE NOBLE GASES. (n.d.). C&EN: IT’S ELEMENTAL: THE PERIODIC TABLE – THE NOBLE GASES. https://pubsapp.acs.org/cen/80th/noblegases.html?
- Noble Gases. (n.d.). Noble Gases. http://butane.chem.uiuc.edu/pshapley/GenChem1/L6/1.html
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. He is a founder of Pediabay and is passionate about helping students through his easily digestible explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.