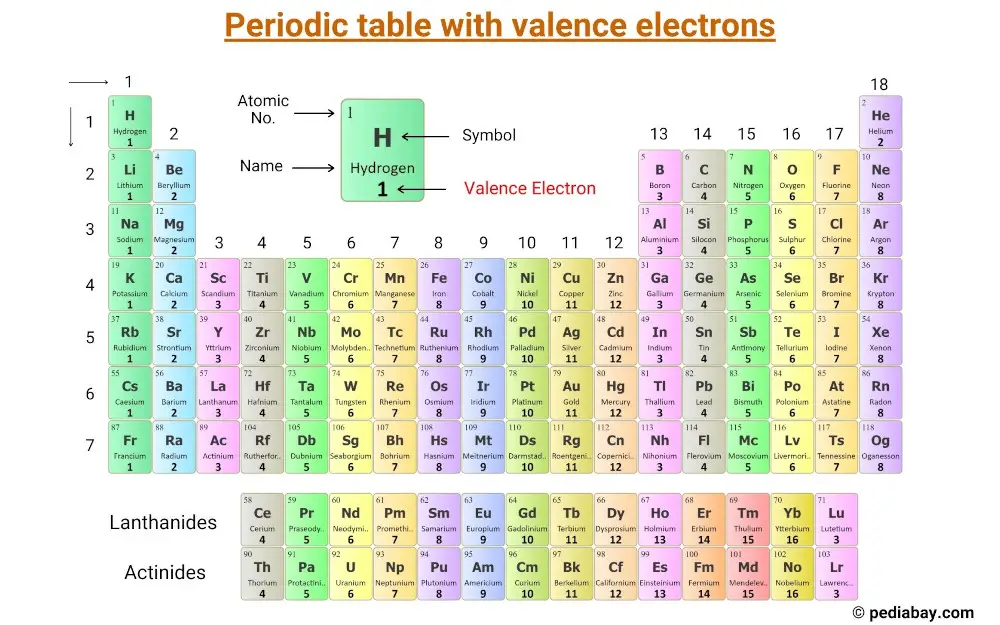
This is a periodic table with valence electrons labeled on it.
Let’s understand the concept of valence electrons as well as the number of valence electrons of main group elements and transition elements.
Table of contents:
- What are valence electrons?
- Valence electrons of main group elements
- Valence electrons of transition and inner-transition elements
What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell or energy level of an atom that are involved in chemical bonding.
For example, magnesium has 2 electrons in its outermost orbit, hence it has 2 valence electrons. [1]
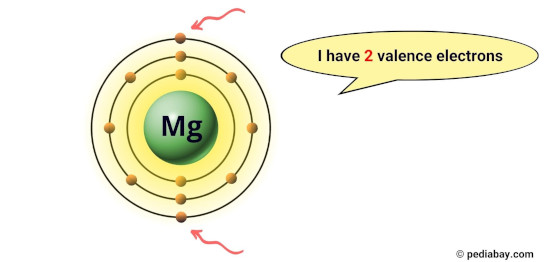
These electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of an element, such as its reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form with other atoms.
The number of valence electrons an atom has determines its position in the periodic table and its ability to form chemical bonds.
Valence electrons of main group elements
The main group elements, also known as the representative elements, are located in groups 1, 2, and 13-18 of the periodic table.
The number of valence electrons in these elements is equal to their group number.
For example, elements in group 1, such as lithium and sodium, have one valence electron, while elements in group 2, such as magnesium and calcium, have two valence electrons.
Elements in group 13, such as boron and aluminum, have three valence electrons, and so on.
These valence electrons are responsible for the elements’ unique chemical properties and reactivity.
Valence electrons of transition and inner-transition elements
Valence electrons of transition elements and inner transition elements are more complicated to determine than those of main group elements.
This is because the d-subshell of transition elements and f-subshell of inner transition elements are incompletely filled and are very close to the outer s-subshell.
As a result, the electrons of both the d-subshell and s-subshell in transition elements and f-subshell and s-subshell in inner transition elements can behave like valence electrons.
For transition elements, the valence electrons can range from 3 to 12 due to the contribution of both the d-subshell and s-subshell electrons. In some cases, the electrons of incomplete d-orbitals are also considered as valence electrons. [2]
Similarly, for inner transition elements (or f-block elements), the valence electrons can range from 3 to 16 due to the contribution of both the f-subshell and s-subshell electrons. [3] The electrons of incomplete d-orbitals may also be considered as valence electrons in some inner transition metals.
It is important to note that for both transition and inner transition elements, the valence electrons are the electrons present in the shells outside the noble gas core.
External resources:
- Valence Electrons. (n.d.). Valence Electrons. https://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch8/index.php
- Valence electron – Wikipedia. (2022, December 28). Valence Electron – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Valence_electron
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. He is a founder of Pediabay and is passionate about helping students through his easily digestible explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.