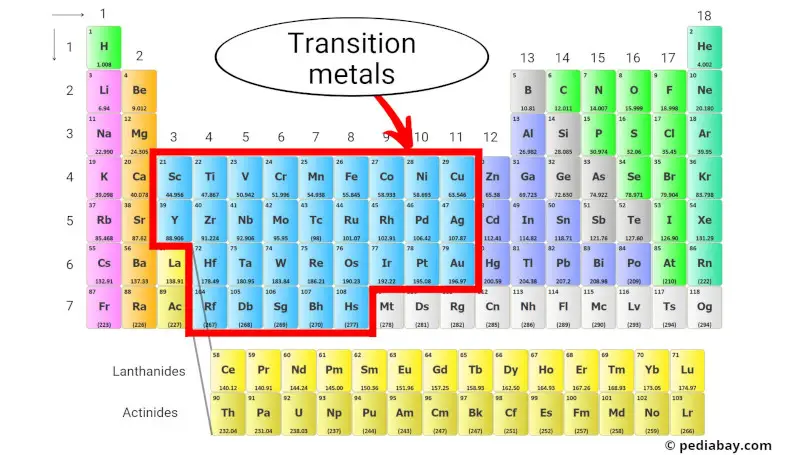
Transition metals are a group of metallic elements found in the middle of the periodic table, specifically from group 3 to 11. [1]
They also have partially filled d-orbitals, which allow them to easily form complex compounds and exhibit a wide range of oxidation states.
Let’s explore more about the transition metals of the periodic table.
Table of contents:
- What are transition metals?
- And why are they called so?
- Facts about transition metals
- Uses of transition metals
- Summary
What are transition metals?
Transition elements (or transition metals) are those elements which have partially filled d-orbitals, either in their elemental form (M) or most common oxidation states (M+, M2+, M3+, etc).
Let me explain this in simple words along with examples.
First of all the elemental state is like this: M;
And the most common oxidation state can be like this: M+, M2+, M3+, etc.
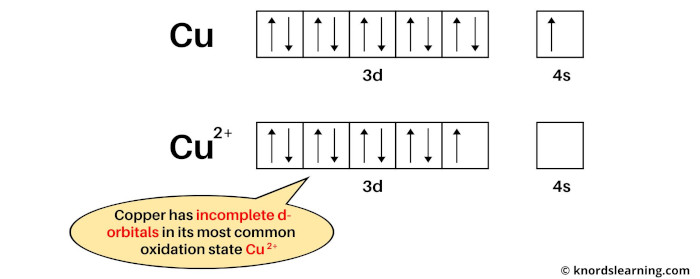
Example 1: Copper
The electron configuration of Cu is: [Ar] 3d10 4s1 and
The electron configuration of Cu2+ is: [Ar] 3d9.
Copper is a transition metal because in its most common oxidation state (Cu2+), it has partially filled d-orbitals.
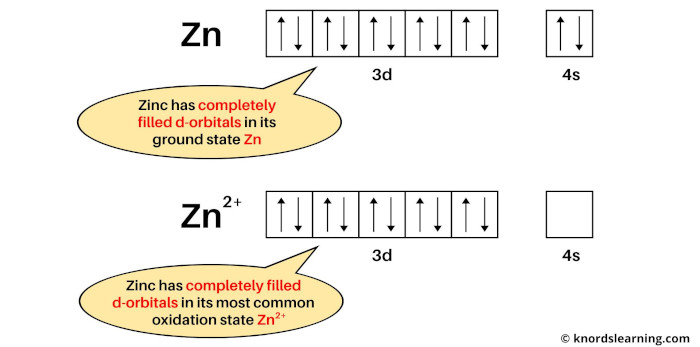
Example 2: Zinc
The electron configuration of Zn is: [Ar] 3d10 4s2 and
The electron configuration of Zn2+ is: [Ar] 3d10.
Zinc is not a transition metal because both its ground state (Zn) and most common oxidation state (Zn2+) have completely filled d-orbitals.
Why are transition metals called so?
Transition metals are called so because their properties reflect a transition in their nature from metallic to nonmetallic as you move from left to right across the periodic table.
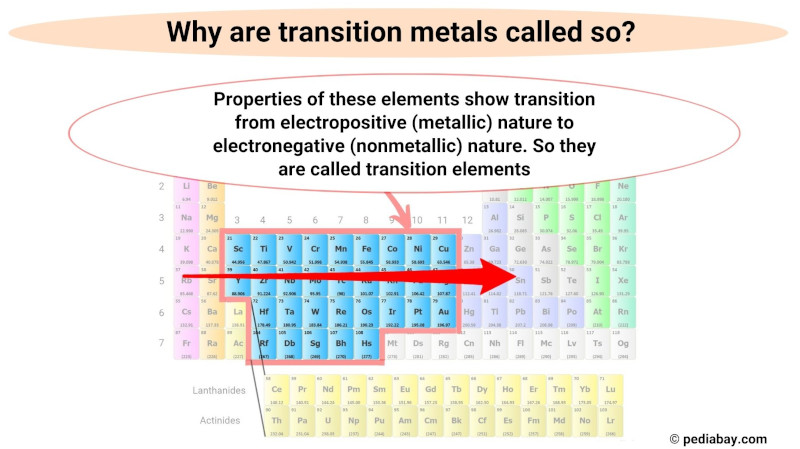
This gradual transition from metallic to nonmetallic behavior is due to the changing electron configuration of the elements as you move from left to right across the block.
The d-orbitals play a key role in this transition, as they can participate in chemical bonding in a variety of ways, leading to the formation of complex ions and compounds.
Facts about transition metals
Here are a few facts about transition metals.
- The transition metals are located in the center of the periodic table, which reflects their unique electronic and chemical properties.
- Some transition metals have multiple oxidation states, which means they can form ions with different charges depending on the reaction conditions.
- Some transition metals are excellent conductors of heat and electricity, making them important in many industrial applications.
- The transition metals have a wide range of oxidation states, allowing them to form a variety of compounds with different chemical properties.
- The transition metals include some of the most valuable and precious metals, such as gold, silver, and platinum, which have important applications in jewelry, currency, and industry.
Uses of transition metals
Here are the uses of a few transition metals.
- Iron is used to make steel, which is used in construction, transportation, and many other industries.
- Copper is used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and other applications that require good conductivity.
- Titanium is used in aerospace and military applications, as well as in medical implants, due to its strength, light weight, and resistance to corrosion.
- Nickel is used in stainless steel and other alloys, as well as in batteries and electroplating.
- Silver is used in jewelry, coins, and other decorative items, as well as in electronics, solar panels, and antibacterial products.
- Gold is used in jewelry, currency, and other decorative items, as well as in electronics, aerospace, and medicine.
- Platinum is used in catalytic converters, jewelry, and other industrial applications due to its resistance to corrosion and ability to catalyze reactions.
- Manganese is used in steelmaking, batteries, and other applications where strong, lightweight metals are needed.
- Cobalt is used in magnets, batteries, and other applications where strong, durable materials are needed.
Summary
Transition metals are a group of metallic elements found in the middle of the periodic table with partially filled d-orbitals that allow them to easily form complex compounds and exhibit a wide range of oxidation states.
Their properties reflect a transition in their nature from metallic to nonmetallic as you move from left to right across the periodic table. Some transition metals have multiple oxidation states and are excellent conductors of heat and electricity.
They include valuable and precious metals such as gold, silver, and platinum. Transition metals are used in various applications such as construction, transportation, electrical wiring, plumbing, aerospace, medicine, and industrial catalytic converters.
External resources:
- Transition metal – Wikipedia. (2021, January 28). Transition Metal – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transition_metal
- Transition_metal. (n.d.). Transition_Metal. http://www.chemeurope.com/en/encyclopedia/Transition_metal.html
- Introducing transition metals. (n.d.). Introducing Transition Metals. http://www.chemguide.co.uk/inorganic/transition/features.html
Jay is an educator and has helped more than 100,000 students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. He is a founder of Pediabay and is passionate about helping students through his easily digestible explanations.
Read more about our Editorial process.